You'Ve Got Fallen Arches?
Overview

Flat feet plague many Americans and perhaps one of the worst times to have fallen arches is the winter holiday season. Why? Many people are destined to spend hours standing in line waiting to pay for holiday gifts, see Santa or mail holiday cards and packages. There are also those cocktail parties, holiday caroling sessions and strolls through the Christmas lights that will undoubtedly have people on their feet for long stretches of time too.
Causes
When flat feet develop at a later age, they are known as fallen arches. The arches may fall because the muscles supporting them are no longer able to do so. In addition the spring ligament within the foot may have lost some of its tension allowing the arch of the foot to flatten. Other conditions causing fallen arches include sudden weight gain, a nervous system injury, or a loss of sensation caused by a disease such as diabetes. Most people with fallen arches are flat on both feet.
Symptoms
Having flat feet can be painless and is actually normal in some people. But others with flat feet experience pain in the heel or arch area, difficulty standing on tiptoe, or have swelling along the inside of the ankle. They may also experience pain after standing for long periods of time or playing sports. Some back problems can also be attributed to flat feet.
Diagnosis
Runners are often advised to get a gait analysis to determine what type of foot they have and so what kind of running shoe they require. This shouldn?t stop at runners. Anyone that plays sports could benefit from this assessment. Sports shoes such as football boots, astro trainers and squash trainers often have very poor arch support and so for the 60-80% of us who do overpronate or have flat feet they are left unsupported. A change of footwear or the insertion of arch support insoles or orthotics can make a massive difference to your risk of injury, to general aches and pains and even to your performance.
How do you get an arch in your foot?
Non Surgical Treatment
When pain results from a fallen arch, the physician may prescribe these. Rest and ice. A brace to help support the fallen arch. Physical therapy to strengthen and stretch the foot. Orthotics (arch supports) to compensate for a fallen arch. The physician may tell the patient to choose shoes that have proper arch supports and avoid non-supportive shoes such as flip-flops. If obesity contributed to the fallen arch, the patient should lose weight.
Surgical Treatment

In cases of flat feet that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required and in some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
Prevention
Sit up straight in a chair with your feet flat on the ground. Scrunch up the toes of one foot as if you are trying to grab hold of the floor then use your toes to drag your foot a small distance forwards. Do this a couple of times on each foot, but don?t use your leg muscles to push your foot forward -- the movement should come solely from the muscles in your feet. Sit in a chair and place a cleaning cloth, towel or small ball on the floor at your feet. Use the toes of one foot to grasp the object and lift it off the floor. This action will require you to clench your toes and contract your arch. Once you have lifted the object a little way off the floor, try to throw it in the air and catch it by stretching your toes and arch out and upwards. Repeat the exercise several times on both feet. Sit on the floor with your legs straight out in front of you then bend your knees out to either side and place the soles of your feet together so your legs form a diamond. Hold on to your ankles and, keeping your heels together at all times, separate your feet so your toes point out to either side. Open and close your feet in this way several times, making sure your little toes stay in contact with the floor throughout the exercise. Starting in the same position, try separating your heels, keeping your toes together at all times.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.

Flat feet plague many Americans and perhaps one of the worst times to have fallen arches is the winter holiday season. Why? Many people are destined to spend hours standing in line waiting to pay for holiday gifts, see Santa or mail holiday cards and packages. There are also those cocktail parties, holiday caroling sessions and strolls through the Christmas lights that will undoubtedly have people on their feet for long stretches of time too.
Causes
When flat feet develop at a later age, they are known as fallen arches. The arches may fall because the muscles supporting them are no longer able to do so. In addition the spring ligament within the foot may have lost some of its tension allowing the arch of the foot to flatten. Other conditions causing fallen arches include sudden weight gain, a nervous system injury, or a loss of sensation caused by a disease such as diabetes. Most people with fallen arches are flat on both feet.
Symptoms
Having flat feet can be painless and is actually normal in some people. But others with flat feet experience pain in the heel or arch area, difficulty standing on tiptoe, or have swelling along the inside of the ankle. They may also experience pain after standing for long periods of time or playing sports. Some back problems can also be attributed to flat feet.
Diagnosis
Runners are often advised to get a gait analysis to determine what type of foot they have and so what kind of running shoe they require. This shouldn?t stop at runners. Anyone that plays sports could benefit from this assessment. Sports shoes such as football boots, astro trainers and squash trainers often have very poor arch support and so for the 60-80% of us who do overpronate or have flat feet they are left unsupported. A change of footwear or the insertion of arch support insoles or orthotics can make a massive difference to your risk of injury, to general aches and pains and even to your performance.
How do you get an arch in your foot?
Non Surgical Treatment
When pain results from a fallen arch, the physician may prescribe these. Rest and ice. A brace to help support the fallen arch. Physical therapy to strengthen and stretch the foot. Orthotics (arch supports) to compensate for a fallen arch. The physician may tell the patient to choose shoes that have proper arch supports and avoid non-supportive shoes such as flip-flops. If obesity contributed to the fallen arch, the patient should lose weight.
Surgical Treatment

In cases of flat feet that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required and in some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
Prevention
Sit up straight in a chair with your feet flat on the ground. Scrunch up the toes of one foot as if you are trying to grab hold of the floor then use your toes to drag your foot a small distance forwards. Do this a couple of times on each foot, but don?t use your leg muscles to push your foot forward -- the movement should come solely from the muscles in your feet. Sit in a chair and place a cleaning cloth, towel or small ball on the floor at your feet. Use the toes of one foot to grasp the object and lift it off the floor. This action will require you to clench your toes and contract your arch. Once you have lifted the object a little way off the floor, try to throw it in the air and catch it by stretching your toes and arch out and upwards. Repeat the exercise several times on both feet. Sit on the floor with your legs straight out in front of you then bend your knees out to either side and place the soles of your feet together so your legs form a diamond. Hold on to your ankles and, keeping your heels together at all times, separate your feet so your toes point out to either side. Open and close your feet in this way several times, making sure your little toes stay in contact with the floor throughout the exercise. Starting in the same position, try separating your heels, keeping your toes together at all times.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.
All The Things You Will Need To Know About
Overview

Heel pain is often a symptom caused by one of two conditions: Plantar Fasciitis or Achilles Tendonitis. Most commonly, heel pain experienced at the bottom of the heel is caused by plantar fasciitis. Heel pain may become so severe for some that just putting weight on their feet first thing in the morning is excruciating. Walking or running may feel completely out of the question.
Causes
Heel pain has many causes. Heel pain is generally the result of faulty biomechanics (walking gait abnormalities) that place too much stress on the heel bone and the soft tissues that attach to it. The stress may also result from injury, or a bruise incurred while walking, running, or jumping on hard surfaces; wearing poorly constructed footwear (such as flimsy flip-flops); or being overweight.
Symptoms
The primary symptom is pain in the heel area that varies in severity and location. The pain is commonly intense when getting out of bed or a chair. The pain often lessens when walking.
Diagnosis
To arrive at a diagnosis, the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the surgeon rules out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. In addition, diagnostic imaging studies such as x-rays or other imaging modalities may be used to distinguish the different types of heel pain. Sometimes heel spurs are found in patients with plantar fasciitis, but these are rarely a source of pain. When they are present, the condition may be diagnosed as plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome.
Non Surgical Treatment
Initially, treatment will consist of adding support to the foot, including better shoes and an over-the-counter arch supports and/or insoles; resting from the sport or activity that aggravates the problem; stretching the calf and arch muscles; taking anti-inflammatory; and using ice and massage to reduce inflammation. You can ice and message your muscles simultaneously by freezing a water bottle filled with water and using it to massage your foot by rolling it underneath your foot for five to 10 minutes at least two times per day. It is not unusual for symptoms of plantar fasciitis to persist for six to 12 months despite treatment.
Surgical Treatment
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
heel spur surgery
Prevention
You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.

Heel pain is often a symptom caused by one of two conditions: Plantar Fasciitis or Achilles Tendonitis. Most commonly, heel pain experienced at the bottom of the heel is caused by plantar fasciitis. Heel pain may become so severe for some that just putting weight on their feet first thing in the morning is excruciating. Walking or running may feel completely out of the question.
Causes
Heel pain has many causes. Heel pain is generally the result of faulty biomechanics (walking gait abnormalities) that place too much stress on the heel bone and the soft tissues that attach to it. The stress may also result from injury, or a bruise incurred while walking, running, or jumping on hard surfaces; wearing poorly constructed footwear (such as flimsy flip-flops); or being overweight.
Symptoms
The primary symptom is pain in the heel area that varies in severity and location. The pain is commonly intense when getting out of bed or a chair. The pain often lessens when walking.
Diagnosis
To arrive at a diagnosis, the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the surgeon rules out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. In addition, diagnostic imaging studies such as x-rays or other imaging modalities may be used to distinguish the different types of heel pain. Sometimes heel spurs are found in patients with plantar fasciitis, but these are rarely a source of pain. When they are present, the condition may be diagnosed as plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome.
Non Surgical Treatment
Initially, treatment will consist of adding support to the foot, including better shoes and an over-the-counter arch supports and/or insoles; resting from the sport or activity that aggravates the problem; stretching the calf and arch muscles; taking anti-inflammatory; and using ice and massage to reduce inflammation. You can ice and message your muscles simultaneously by freezing a water bottle filled with water and using it to massage your foot by rolling it underneath your foot for five to 10 minutes at least two times per day. It is not unusual for symptoms of plantar fasciitis to persist for six to 12 months despite treatment.
Surgical Treatment
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
heel spur surgery
Prevention

You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.
Limb-Length Discrepancy After Hip Arthroplasty
Overview
Leg length discrepancy (LLD) or Lower limb discrepancy is a condition of unequal lengths of the lower limbs. The discrepancy may be in the femur, or tibia, or both. In some conditions, the whole side is affected, including the upper limbs. However, it is the discrepancy of the lower limbs that causes problems with ambulation, and the focus of this discussion will be about lower limb discrepancy.
Causes
Common causes include bone infection, bone diseases, previous injuries, or broken bones. Other causes may include birth defects, arthritis where there is a loss of articular surface, or neurological conditions.
Symptoms
Many people walk around with LLD?s of up to 2 cm. and not even know it. However, discrepancies above 2 cm. becomes more noticeable, and a slight limp is present. But even up to 3 cm. a small lift compensates very well, and many patients are quite happy with this arrangement. Beyond 3 cm. however, the limp is quite pronounced, and medical care is often sought at that point. Walking with a short leg gait is not only unsightly, but increases energy expenditure during ambulation. It could also put more stress on the long leg, and causes functional scoliosis. Where the discrepancy is more severe, walking becomes grotesque or virtually impossible.
Diagnosis
The doctor carefully examines the child. He or she checks to be sure the legs are actually different lengths. This is because problems with the hip (such as a loose joint) or back (scoliosis) can make the child appear to have one shorter leg, even though the legs are the same length. An X-ray of the child?s legs is taken. During the X-ray, a long ruler is put in the image so an accurate measurement of each leg bone can be taken. If an underlying cause of the discrepancy is suspected, tests are done to rule it out.
Non Surgical Treatment
The non-surgical intervention is mainly usedfor the functional and environmental types of leg length discrepancies. It is also applied to the mild category of limb length inequality. Non-surgical intervention consists of stretching the muscles of the lower extremity. This is individually different, whereby the M. Tensor Fascia latae, the adductors, the hamstring muscles, M. piriformis and M. Iliopsoas are stretched. In this non-surgical intervention belongs also the use of shoe lifts. These shoe lifts consists of either a shoe insert (up to 10-20mm of correction), or building up the sole of the shoe on the shorter leg (up to 30-60mm of correction). This lift therapy should be implemented gradually in small increments. Several studies have examined the treatment of low back pain patients with LLD with shoe lifts. Gofton obtained good results: the patients experienced major or complete pain relief that lasted upon follow-up ranging from 3 to 11 years. Helliwell also observed patients whereby 44% experienced complete pain relief, and 45% had moderate or substantial pain relief. Friberg found that 157 (of 211) patients with LBP, treated with shoe lifts, were symprom-free after a mean follow-up of 18 months.

how to increase height naturally after 21
Surgical Treatment
Many people undergo surgery for various reasons - arthritis, knee replacement, hip replacement, even back surgery. However, the underlying cause of leg length inequality still remains. So after expensive and painful surgery, follow by time-consuming and painful rehab, the true culprit still remains. Resuming normal activities only continues to place undue stress on the already overloaded side. Sadly so, years down the road more surgeries are recommended for other joints that now endure the excessive forces.
Leg length discrepancy (LLD) or Lower limb discrepancy is a condition of unequal lengths of the lower limbs. The discrepancy may be in the femur, or tibia, or both. In some conditions, the whole side is affected, including the upper limbs. However, it is the discrepancy of the lower limbs that causes problems with ambulation, and the focus of this discussion will be about lower limb discrepancy.

Causes
Common causes include bone infection, bone diseases, previous injuries, or broken bones. Other causes may include birth defects, arthritis where there is a loss of articular surface, or neurological conditions.
Symptoms
Many people walk around with LLD?s of up to 2 cm. and not even know it. However, discrepancies above 2 cm. becomes more noticeable, and a slight limp is present. But even up to 3 cm. a small lift compensates very well, and many patients are quite happy with this arrangement. Beyond 3 cm. however, the limp is quite pronounced, and medical care is often sought at that point. Walking with a short leg gait is not only unsightly, but increases energy expenditure during ambulation. It could also put more stress on the long leg, and causes functional scoliosis. Where the discrepancy is more severe, walking becomes grotesque or virtually impossible.
Diagnosis
The doctor carefully examines the child. He or she checks to be sure the legs are actually different lengths. This is because problems with the hip (such as a loose joint) or back (scoliosis) can make the child appear to have one shorter leg, even though the legs are the same length. An X-ray of the child?s legs is taken. During the X-ray, a long ruler is put in the image so an accurate measurement of each leg bone can be taken. If an underlying cause of the discrepancy is suspected, tests are done to rule it out.
Non Surgical Treatment
The non-surgical intervention is mainly usedfor the functional and environmental types of leg length discrepancies. It is also applied to the mild category of limb length inequality. Non-surgical intervention consists of stretching the muscles of the lower extremity. This is individually different, whereby the M. Tensor Fascia latae, the adductors, the hamstring muscles, M. piriformis and M. Iliopsoas are stretched. In this non-surgical intervention belongs also the use of shoe lifts. These shoe lifts consists of either a shoe insert (up to 10-20mm of correction), or building up the sole of the shoe on the shorter leg (up to 30-60mm of correction). This lift therapy should be implemented gradually in small increments. Several studies have examined the treatment of low back pain patients with LLD with shoe lifts. Gofton obtained good results: the patients experienced major or complete pain relief that lasted upon follow-up ranging from 3 to 11 years. Helliwell also observed patients whereby 44% experienced complete pain relief, and 45% had moderate or substantial pain relief. Friberg found that 157 (of 211) patients with LBP, treated with shoe lifts, were symprom-free after a mean follow-up of 18 months.

how to increase height naturally after 21
Surgical Treatment
Many people undergo surgery for various reasons - arthritis, knee replacement, hip replacement, even back surgery. However, the underlying cause of leg length inequality still remains. So after expensive and painful surgery, follow by time-consuming and painful rehab, the true culprit still remains. Resuming normal activities only continues to place undue stress on the already overloaded side. Sadly so, years down the road more surgeries are recommended for other joints that now endure the excessive forces.
Mortons Neuroma Causes
Overview
 Patients with Morton?s neuroma present with pain in the forefoot, particularly in the ?ball? of the foot. However, not all pain in the forefoot is a Morton?s neuroma. In fact, most chronic pain in the forefoot is NOT the result of a Morton?s neuroma, but rather is from metatarsalgia - inflammation (synovitis) of the ?toe/foot? joints. The symptoms from Morton?s neuroma are due to irritation to the small digital nerves, as they pass across the sole of the foot and into the toes. Therefore, with a true Morton?s neuroma, it is not uncommon to have nerve-type symptoms, which can include numbness or a burning sensation extending into the toes. There are several interdigital nerves in the forefoot. The most common nerve to develop into a neuroma is between the 3rd and 4th toes. With a true neuroma, the pain should be isolated to just one or two toes.
Patients with Morton?s neuroma present with pain in the forefoot, particularly in the ?ball? of the foot. However, not all pain in the forefoot is a Morton?s neuroma. In fact, most chronic pain in the forefoot is NOT the result of a Morton?s neuroma, but rather is from metatarsalgia - inflammation (synovitis) of the ?toe/foot? joints. The symptoms from Morton?s neuroma are due to irritation to the small digital nerves, as they pass across the sole of the foot and into the toes. Therefore, with a true Morton?s neuroma, it is not uncommon to have nerve-type symptoms, which can include numbness or a burning sensation extending into the toes. There are several interdigital nerves in the forefoot. The most common nerve to develop into a neuroma is between the 3rd and 4th toes. With a true neuroma, the pain should be isolated to just one or two toes.
Causes
The exact cause is as yet unclear. However there are a number of theories. Some expert s believe problems with the design of the foot makes some people more prone to Morton?s neuroma. Having flat feet or a high arch for example encourages the foot to slide forwards which can put excess pressure on the metatarsals. Bunions and hammer toes also increase the likelihood of developing Morton?s. However simply wearing high heels or any form of tight shoes that put pressure on the bones in the feet can also lead to a Morton?s . Typically the condition comes on between the age of 40 and 50. It is far more common in women than men - three out of four sufferers are women.
Symptoms
Episodes of pain are intermittent. Patients may experience 2 attacks in a week and then none for a year. Recurrences are variable and tend to become more frequent. Between attacks, no symptoms or physical signs occur. Two neuromas coexist on the same foot about 2-3% of the time. Other diagnoses should be considered when 2 or more areas of tenderness are present.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will suspect that you have a Morton's neuroma based on the nature and location of your foot pain. He or she may ask questions about your shoes - what type of shoes you usually wear and whether these shoes have narrow toes or high heels. To rule out other causes of foot pain, your doctor may ask questions about your medical history, especially any history of arthritis, nerve and muscle problems or previous injury to your foot or leg.
Non Surgical Treatment
Symptoms of a Morton's neuroma can completely resolve with simple treatments, such as resting the foot, better-fitting shoes, anti-inflammation medications, and ice packs. More rapid relief of symptoms can follow a local cortisone injection. Symptoms can progressively worsen with time. For those with persistent symptoms, the swollen nerve tissue is removed with a surgical operation.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to excise the neuroma is usually performed under general anaesthetic in a day surgery facility. After surgery you will have to keep your foot dry for two weeks. Generally neuroma surgery allows for early weight bearing and protection in some type of post op shoe gear. Some neuromas may reoccur, but this is rare. Most studies on patient satisfaction after neuroma surgery show approximately 90% reduction of pain and about 85% of all patients rated the overall satisfaction with the results as excellent or good.
Prevention
Although the exact causes of neuromas are not completely known, the following preventive steps may help. Make sure your exercise shoes have enough room in the front part of the shoe and that your toes are not excessively compressed. Wear shoes with adequate padding in the ball of the foot. Avoid prolonged time in shoes with a narrow toe box or excessive heel height (greater than two inches).
 Patients with Morton?s neuroma present with pain in the forefoot, particularly in the ?ball? of the foot. However, not all pain in the forefoot is a Morton?s neuroma. In fact, most chronic pain in the forefoot is NOT the result of a Morton?s neuroma, but rather is from metatarsalgia - inflammation (synovitis) of the ?toe/foot? joints. The symptoms from Morton?s neuroma are due to irritation to the small digital nerves, as they pass across the sole of the foot and into the toes. Therefore, with a true Morton?s neuroma, it is not uncommon to have nerve-type symptoms, which can include numbness or a burning sensation extending into the toes. There are several interdigital nerves in the forefoot. The most common nerve to develop into a neuroma is between the 3rd and 4th toes. With a true neuroma, the pain should be isolated to just one or two toes.
Patients with Morton?s neuroma present with pain in the forefoot, particularly in the ?ball? of the foot. However, not all pain in the forefoot is a Morton?s neuroma. In fact, most chronic pain in the forefoot is NOT the result of a Morton?s neuroma, but rather is from metatarsalgia - inflammation (synovitis) of the ?toe/foot? joints. The symptoms from Morton?s neuroma are due to irritation to the small digital nerves, as they pass across the sole of the foot and into the toes. Therefore, with a true Morton?s neuroma, it is not uncommon to have nerve-type symptoms, which can include numbness or a burning sensation extending into the toes. There are several interdigital nerves in the forefoot. The most common nerve to develop into a neuroma is between the 3rd and 4th toes. With a true neuroma, the pain should be isolated to just one or two toes.Causes
The exact cause is as yet unclear. However there are a number of theories. Some expert s believe problems with the design of the foot makes some people more prone to Morton?s neuroma. Having flat feet or a high arch for example encourages the foot to slide forwards which can put excess pressure on the metatarsals. Bunions and hammer toes also increase the likelihood of developing Morton?s. However simply wearing high heels or any form of tight shoes that put pressure on the bones in the feet can also lead to a Morton?s . Typically the condition comes on between the age of 40 and 50. It is far more common in women than men - three out of four sufferers are women.
Symptoms
Episodes of pain are intermittent. Patients may experience 2 attacks in a week and then none for a year. Recurrences are variable and tend to become more frequent. Between attacks, no symptoms or physical signs occur. Two neuromas coexist on the same foot about 2-3% of the time. Other diagnoses should be considered when 2 or more areas of tenderness are present.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will suspect that you have a Morton's neuroma based on the nature and location of your foot pain. He or she may ask questions about your shoes - what type of shoes you usually wear and whether these shoes have narrow toes or high heels. To rule out other causes of foot pain, your doctor may ask questions about your medical history, especially any history of arthritis, nerve and muscle problems or previous injury to your foot or leg.
Non Surgical Treatment
Symptoms of a Morton's neuroma can completely resolve with simple treatments, such as resting the foot, better-fitting shoes, anti-inflammation medications, and ice packs. More rapid relief of symptoms can follow a local cortisone injection. Symptoms can progressively worsen with time. For those with persistent symptoms, the swollen nerve tissue is removed with a surgical operation.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery to excise the neuroma is usually performed under general anaesthetic in a day surgery facility. After surgery you will have to keep your foot dry for two weeks. Generally neuroma surgery allows for early weight bearing and protection in some type of post op shoe gear. Some neuromas may reoccur, but this is rare. Most studies on patient satisfaction after neuroma surgery show approximately 90% reduction of pain and about 85% of all patients rated the overall satisfaction with the results as excellent or good.
Prevention
Although the exact causes of neuromas are not completely known, the following preventive steps may help. Make sure your exercise shoes have enough room in the front part of the shoe and that your toes are not excessively compressed. Wear shoes with adequate padding in the ball of the foot. Avoid prolonged time in shoes with a narrow toe box or excessive heel height (greater than two inches).
Are Shoe Lifts The Ideal Solution To Leg Length Difference
There are two different kinds of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital means that you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter compared to the other. Through developmental periods of aging, the brain picks up on the walking pattern and recognizes some variation. The body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch is not grossly abnormal, does not need Shoe Lifts to compensate and ordinarily does not have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this condition is simply corrected, and can eliminate a number of incidents of lumbar pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly consists of Shoe Lifts . These are very inexpensive, ordinarily costing less than twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or even more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most widespread condition afflicting men and women today. Around 80 million men and women are afflicted by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses huge amounts of money yearly as a result of time lost and production. New and better treatment methods are always sought after in the hope of lowering economic impact this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the earth suffer from foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In most of these cases Shoe Lifts can be of worthwhile. The lifts are capable of eliminating any pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous expert orthopaedic orthopedists.
So that they can support the body in a well balanced fashion, feet have a vital task to play. In spite of that, it is sometimes the most neglected region of the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that appropriate posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this condition is simply corrected, and can eliminate a number of incidents of lumbar pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly consists of Shoe Lifts . These are very inexpensive, ordinarily costing less than twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or even more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most widespread condition afflicting men and women today. Around 80 million men and women are afflicted by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem which costs businesses huge amounts of money yearly as a result of time lost and production. New and better treatment methods are always sought after in the hope of lowering economic impact this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the earth suffer from foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In most of these cases Shoe Lifts can be of worthwhile. The lifts are capable of eliminating any pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous expert orthopaedic orthopedists.
So that they can support the body in a well balanced fashion, feet have a vital task to play. In spite of that, it is sometimes the most neglected region of the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that appropriate posture and balance are restored.
What Causes Posterior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
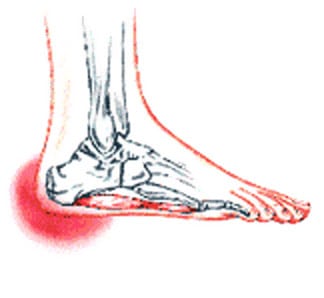
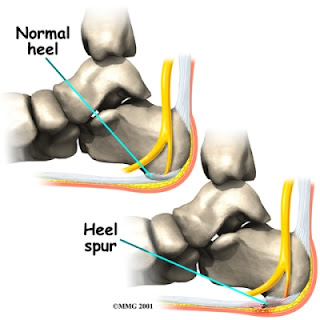
A heel spur is a calcium deposit on the underside of the heel bone. Heel spurs are related to plantar fasciitis in that both are caused by irritation and lack of support of the plantar ligaments. Your plantar ligaments are a band of connective tissue that extend along the bottom of the foot and connect your heel bone to the ball of your foot.
Causes
When a bone is subjected to pressure, rubbing, or other stress over long periods, it tries to repair itself by building extra bone. This extra bone is what is referred to as a ?spur?. Many form as part of the aging process when cartilage breaks down in the joints.

Symptoms
The following symptoms are typical of heel spur. Stabbing pain when treading on the area affected. Dull, irregularly occurring pains in the heel area also without exerting pressure (e.g. in a reclining position) Pain when taking the first steps in the morning (after lying or sitting down for an extended period, especially in the morning) Occasional swelling in the ankle area. For the lower heel spur, extreme sensitivity at the tendon attachment (laterally in the lower heel area) For the upper heel spur, extreme pressure sensitivity of the Achilles tendon, primarily at approximately ankle height.
Diagnosis
Because the diagnosis of heel spurs can be confused with tarsal tunnel syndrome (as described earlier), most surgeons advocate performing a tarsal tunnel release (or at least a partial tarsal tunnel release) along with the plantar fascia release. This surgery is about 80percent successful in relieving pain in the small group of patients who do not improve with conservative treatments.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are many temporary solutions to resolve the pain associated with irritation to the plantar ligaments. Common recommendations are ice and anti-inflammatory medications or even cortisone injections, however none of these solve the fundamental problem. To permanently resolve heel spurs you need to support and restrict the movement of the plantar ligaments. Flexible shoes will aggravate and often contribute to heel spurs. We recommend a RIGID orthotic that extends from the metatarsal heads to the heel to resolve heel spurs.
Surgical Treatment
Heel spur surgery should only be considered after less invasive treatment methods have been explored and ruled insufficient. The traditional surgical approach to treating heel spurs requires a scalpel cut to the bottom of the food which allows the surgeon to access the bone spur. Endoscopic plantar fasciotomies (EPF) involve one or two small incisions in the foot which allow the surgeon to access and operate on the bone spur endoscopically. Taking a surgical approach to heel spur treatment is a topic to explore with a foot and ankle specialist.
Prevention
You can help prevent heel spur symptoms from returning by wearing the proper shoes. Customized orthotics and insoles can help relieve pressure. It is important to perform your exercises to help keep your foot stretched and relaxed.
What Can Induce Posterior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
The plantar fascia is connective tissue on the sole of your foot. When the arch of the foot is not properly supported, the plantar fascia can stretch and pull away from the heel area. When the plantar fascia pulls away from the heel, calcium deposits form in its absence. These calcium deposits are called heel spurs and can be very painful.
Causes
Heel spurs can be caused by several things. Anything that can cause the body to rebuild itself can lead to a bone spur. A heel spur is a natural reaction of the body to correct a weakness by building extra bone. One of the most common causes for the development of heel spurs is the wearing of shoes that are too tight. That?s why more women suffer from heel spurs more than men. Athletes who tend to stress their feet a lot, people are overweight who have more pressure on their lower extremities and the elderly also tend to suffer more from heel spurs.
Symptoms
The spur itself is not painful, however, if it is sharp and pointed it can poke into soft tissue surrounding the spur itself. As the bone spur irritates the tissue, inflammation and bruising can occur leading to heel pain. Heel spurs can affect your ability to do your usual work and/or activities, and can also trap and irritate the nerves in your heel area. They can change the way you walk, and can lead to knee, hip and low back injuries. If severe, they may require medical intervention.
Diagnosis
Heel spurs and plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by your physiotherapist or sports doctor based on your symptoms, history and clinical examination. After confirming your heel spur or plantar fasciitis they will investigate WHY you are likely to be predisposed to heel spurs and develop a treatment plan to decrease your chance of future bouts. X-rays will show calcification or bone within the plantar fascia or at its insertion into the calcaneus. This is known as a calcaneal or heel spur. Ultrasound scans and MRI are used to identify any plantar fasciitis tears, inflammation or calcification. Pathology tests may identify spondyloarthritis, which can cause symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
To aid in the reduction of inflammation, applying ice for 10-15 minutes after activities and the use of anti-inflammatory medications, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, can be helpful. Corticosteroid injections may also be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy can be beneficial with the use of heat modalities, such as ultrasound, that create a deep heat and reduce inflammation. If the pain caused by inflammation is constant, keeping the foot raised above the heart and/or compressed by wrapping with a bandage will help. Taping can help speed the healing process by protecting the fascia from reinjury, especially during stretching and walking.
Surgical Treatment
Though conservative treatments for heel spurs work most of the time, there are some cases where we need to take your treatment to the next level. Luckily, with today?s technologies, you can still often avoid surgery. Some of the advanced technologies to treat a Heel Spur are Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy. Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy (also known as PRP) is one of several regenerative medicine techniques that University Foot and Ankle Institute has helped bring to foot and ankle care. This amazing in-office procedure allows the growth factors in the blood to be used to actually begin the healing process again long after your body has given up on healing the area. Heel Pain Shockwave Therapy. Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive procedure done in the office that allows for new blood to get to the region of fascia damage and help with healing. Results have been excellent with more than 70 percent of patients getting relief with only one treatment. Topaz for Heal Spurs and pain. Another minimally invasive technology technique is called Coblation Surgery using a Topaz probe. This minimally invasive procedure involves controlled heating of multiple tiny needles that are inserted through the skin and into the plantar fascia. This process, like PRP and Shockwave therapy, irritates the fascia enough to turn a chronic problem back into an acute problem, greatly increasing the chances of healing. Heel Spur Surgery. Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy is one surgical procedure that we consider to release the tight fascia. University Foot and Ankle Institute has perfected an endoscopic (camera guided) approach for fascia release to allow rapid healing and limited downtime with minimal pain.